Spaghetti Models
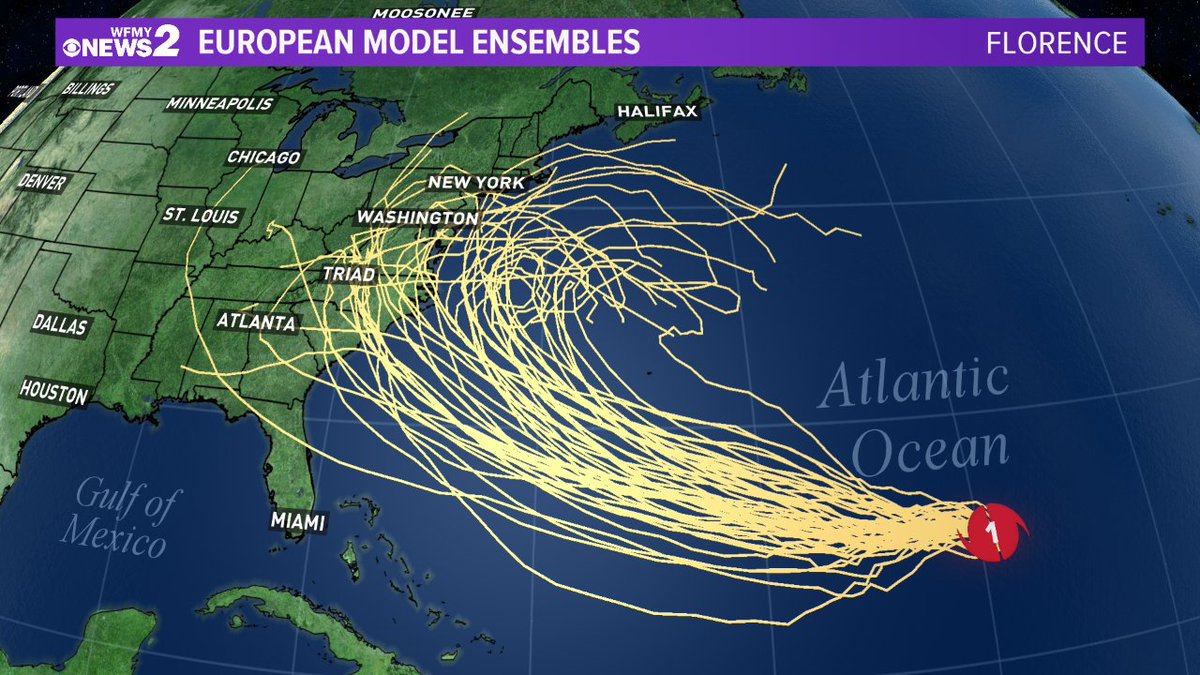
Spaghetti models are complex computer simulations used to predict the behavior of complex systems. They are called “spaghetti models” because the output of the model is often a spaghetti-like tangle of lines representing the possible outcomes.
Spaghetti models are a great way to visualize the potential paths of a storm. They show a range of possible tracks, which can help forecasters and emergency managers make better decisions. For example, the tropical storm beryl spaghetti models showed a wide range of possible tracks for the storm, which helped forecasters issue more accurate warnings.
Spaghetti models are used in a variety of applications, including finance, risk management, and engineering. In finance, spaghetti models are used to predict the future value of stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. In risk management, spaghetti models are used to assess the risk of natural disasters, financial crises, and other events. In engineering, spaghetti models are used to design and test new products and systems.
Real-World Examples, Spaghetti models
One of the most famous examples of a spaghetti model is the climate model used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The IPCC’s climate model is a complex computer simulation that predicts the future climate of the Earth. The model takes into account a variety of factors, including the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth, and the behavior of the oceans.
The IPCC’s climate model has been used to predict the future climate of the Earth under a variety of different scenarios. The model has predicted that the Earth’s climate will warm by 1.5 to 2.5 degrees Celsius by the end of the century. The model has also predicted that the warming will lead to more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Spaghetti models, computer simulations that predict hurricane paths, are a valuable tool for forecasting. Want to know if Beryl will hit Florida? Check out will beryl hit florida. These models provide critical information to help residents prepare and make informed decisions.
By integrating data from various sources, spaghetti models offer insights into the potential path and intensity of hurricanes, enabling us to better understand and respond to these powerful storms.
Advantages and Limitations of Spaghetti Models
![]()
Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble models, offer a unique approach to data analysis by combining multiple models into a single, more robust and accurate predictor. This technique leverages the strengths of different modeling algorithms to mitigate individual weaknesses, resulting in improved performance.
Advantages of Spaghetti Models
The advantages of using spaghetti models include:
- Flexibility: Spaghetti models can be easily adapted to different types of data and modeling problems, making them a versatile tool for data analysis.
- Adaptability: By combining multiple models, spaghetti models can capture complex relationships and non-linear patterns in data that individual models may miss.
- Improved accuracy: By leveraging the collective knowledge of multiple models, spaghetti models often achieve higher accuracy than individual models, especially in situations with limited or noisy data.
Limitations of Spaghetti Models
Despite their advantages, spaghetti models also have some limitations:
- Potential for overfitting: Combining multiple models can increase the risk of overfitting, especially if the individual models are not carefully selected and tuned.
- Sensitivity to data quality: Spaghetti models can be sensitive to the quality of the data used for training, and poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate predictions.
- Computational cost: Training and evaluating spaghetti models can be computationally expensive, especially for large datasets or complex models.
Comparison to Other Modeling Techniques
Compared to other modeling techniques, spaghetti models offer several strengths:
- Flexibility: Spaghetti models can be easily adapted to different types of data and modeling problems, making them more versatile than many other techniques.
- Improved accuracy: By combining multiple models, spaghetti models often achieve higher accuracy than individual models, especially in situations with limited or noisy data.
However, spaghetti models also have some weaknesses:
- Potential for overfitting: Spaghetti models can be more prone to overfitting than other techniques, especially if the individual models are not carefully selected and tuned.
- Sensitivity to data quality: Spaghetti models can be sensitive to the quality of the data used for training, and poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate predictions.
- Computational cost: Training and evaluating spaghetti models can be computationally expensive, especially for large datasets or complex models.
Spaghetti Models in Practice
Spaghetti models, with their iterative and exploratory nature, provide a valuable tool for decision-making in complex and uncertain environments. Their practical implementation involves a structured approach, encompassing data collection, model creation, validation, and interpretation.
Step-by-Step Guide for Creating and Implementing Spaghetti Models
- Define the Problem and Objectives: Clearly articulate the problem or decision to be addressed and establish specific objectives for the spaghetti model.
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data from multiple sources, ensuring it is comprehensive, reliable, and representative of the problem domain.
- Model Creation: Develop multiple alternative models, each representing a different perspective or hypothesis. These models can range from simple linear regressions to complex simulation models.
- Model Validation: Evaluate the performance of each model using statistical measures, historical data, or expert judgment. This step ensures the models are reliable and produce reasonable results.
- Model Selection: Based on the validation results, select the model or combination of models that best meet the objectives and provide the most useful insights.
- Scenario Analysis: Use the selected model to explore different scenarios and assess the potential impact of various decisions or actions.
- Interpretation and Decision-Making: Analyze the results of the scenario analysis to identify key insights, patterns, and potential risks. Use this information to inform decision-making and develop strategies.
Tips and Best Practices for Developing Effective Spaghetti Models
- Involve a diverse team with expertise in different areas to provide multiple perspectives.
- Encourage creativity and experimentation in model creation to explore a wide range of possibilities.
- Use visualization tools to communicate the results of the spaghetti model in a clear and accessible way.
- Continuously monitor and update the spaghetti model as new data or insights become available.
Example of a Spaghetti Model Using a Real-World Dataset
Consider a company facing a decision on whether to invest in a new product line. The company creates multiple spaghetti models, each with different assumptions about market demand, production costs, and competitive factors. The models are validated using historical data and expert opinions. The selected model indicates a potential for significant profitability, leading the company to decide to invest in the new product line.
Demonstrating the Interpretation of Spaghetti Model Results for Decision-Making
The spaghetti model results show a range of possible outcomes, from high profitability to potential losses. The decision-makers carefully consider the distribution of outcomes and the associated risks. They decide to invest in the new product line, as the potential upside outweighs the potential downside, and they have developed strategies to mitigate the risks.